Table of Contents
Baphomet, a symbol enshrouded in mysticism and controversy, has intrigued and bewildered scholars, occultists, and the curious alike. This article delves into the multifaceted origins, historical significance, and modern interpretations of Baphomet, exploring the diverse ways this enigmatic figure has left an indelible mark on the realms of the occult and popular culture.
The Origins of Baphomet
Historical Roots
Baphomet’s origins trace back to medieval times, where it was associated with the Knights Templar. Initially depicted as a goat-headed deity, Baphomet’s symbolism evolved over centuries, merging various cultural, alchemical, and occult elements into a complex and elusive figure.
Alchemical Symbolism
In alchemy, Baphomet embodies the union of opposites, representing the reconciliation of spiritual and material realms. The dual nature of Baphomet mirrors the alchemical pursuit of transcending duality to achieve spiritual enlightenment.
Baphomet is Remade in the 19th Century
In the 19th century, Baphomet underwent a transformative remaking, propelled by the visionary pen of occultist Eliphas Lévi. Lévi, seeking to encapsulate mystical equilibrium, reimagined Baphomet in a now-iconic illustration that would become a cornerstone in Western occultism.
Lévi’s Visionary Redesign
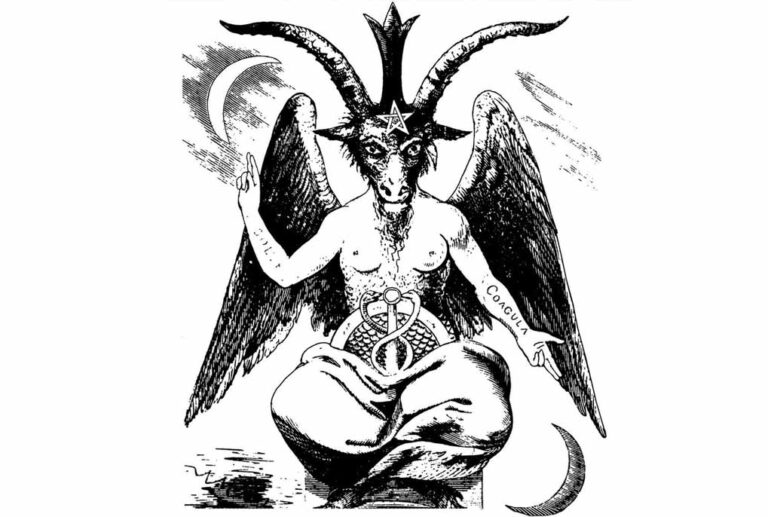
Eliphas Lévi envisioned Baphomet as a hermaphroditic figure, synthesizing masculine and feminine energies. In his depiction, the goat-headed deity, seated within an inverted pentagram, became a visual representation of the reconciliation of opposites – a core tenet in alchemical philosophy.
Symbolic Elements
Lévi meticulously incorporated symbolic elements into his rendition. Baphomet’s right hand pointed upwards, adorned with the sign of spiritual ascent, while the left hand gestured downwards, symbolizing the descent into the material realm. The torch between its horns signified divine enlightenment, emphasizing the pursuit of mystical knowledge.
Transcending Duality
The transformative aspect of Lévi’s remaking lay in Baphomet’s ability to transcend duality. The amalgamation of human, animal, and celestial features reflected the alchemical principle of achieving spiritual enlightenment by harmonizing opposing forces. This representation was a departure from historical depictions and propelled Baphomet into a symbol of profound mystical significance.
Influence on Occult Practices
Lévi’s Baphomet became a catalyst for the resurgence of interest in occult practices. Secret societies and esoteric traditions adopted this redesigned symbol, interpreting it as a key to unlocking hidden knowledge and attaining spiritual balance. The emblematic power of Baphomet, as envisioned by Lévi, reverberated across mystical circles, leaving an indelible mark on occult symbolism.
Legacy and Interpretations
The 19th-century remaking of Baphomet remains a pivotal moment in the evolution of occult iconography. Furthermore, its legacy endures, with contemporary practitioners drawing inspiration from Lévi’s visionary depiction. Consequently, Baphomet, remade in the crucible of the 19th century, continues to be a dynamic and enigmatic symbol, inviting seekers of esoteric wisdom to delve into its layers of meaning and mystery.
Origin of the Myth

The origin of the Baphomet myth is complex and layered, with historical roots intertwined in medieval Christian narratives and later interpretations by occultists. The term “Baphomet” is believed to have been used in relation to the Knights Templar, a medieval Christian military order founded in the 12th century.
Knights Templar Connection
The first documented mention of Baphomet is found in the trials of the Knights Templar during the early 14th century. The Templars, accused of heresy and various crimes, were alleged to have worshipped a mysterious idol named Baphomet. However, historical records are ambiguous, and scholars debate whether Baphomet was an actual entity or a fabrication by the Templars’ accusers.
Symbolic Interpretations
The etymology of the word “Baphomet” remains uncertain, adding to the enigma surrounding its origin. Some theories suggest a derivation from the Old French words “Baph” and “Met,” possibly alluding to baptism and wisdom. Others propose connections to Arabic terms or occult symbolism.
Alchemical and Hermetic Influences
In the centuries following the Knights Templar trials, Baphomet gained symbolic significance in various esoteric traditions. Alchemists and Hermetic scholars incorporated the concept of Baphomet into their mystical frameworks, associating it with the union of opposing forces and the pursuit of spiritual enlightenment.
Eliphas Lévi’s Interpretation
The most influential reinterpretation of Baphomet occurred in the 19th century through the works of the French occultist Eliphas Lévi. Consequently, in his influential illustration, Lévi transformed Baphomet into a hermaphroditic figure. Seated within an inverted pentagram, the depiction embodied the alchemical reconciliation of opposites and the balance between spiritual and material realms.
Contemporary Occultism
Baphomet’s myth has endured and transformed in contemporary occultism. Furthermore, the symbol is commonly linked to diverse interpretations, encompassing the embodiment of divine wisdom, the pursuit of esoteric knowledge, and the representation of a cosmic principle. As a result, it has evolved into a potent and multi-faceted symbol, transcending its historical origins.
The origin of the Baphomet myth remains veiled in historical uncertainties and speculative interpretations. This ambiguity adds to its mystique and enduring allure within the realms of occultism and esoteric thought.
Baphomet in Occultism:

Eliphas Lévi’s Influence:
In the 19th century, occultist Eliphas Lévi depicted Baphomet in his famous illustration, thereby associating it with magical equilibrium. Consequently, Lévi’s depiction became a cornerstone in Western occultism, exerting a profound influence on subsequent esoteric traditions and secret societies.
Modern Occult Practices:
Baphomet remains a potent symbol in modern occultism, and it has been adopted by various magical traditions, secret societies, and practitioners of ritual magic. Furthermore, its symbolism continues to inspire mystery and intrigue. Each practitioner interprets its meaning through their own esoteric lens, adding to the diversity of perspectives surrounding this enigmatic symbol.
Controversies and Misconceptions:
Satanic Panic:
Baphomet became a focal point during the Satanic Panic of the 1980s, wrongly associated with Satanism and occult rituals. This period saw widespread fear and misinformation surrounding Baphomet, leading to its vilification in popular culture.
Legal Battles:
In recent years, Baphomet has been at the center of legal disputes. The Satanic Temple, a nontheistic religious organization, employed a Baphomet statue in their advocacy for the separation of church and state, sparking legal battles and debates on religious freedom.
Baphomet in Popular Culture:

Music and Art:
Baphomet’s influence permeates popular culture, particularly in music, art, and literature. From album covers to contemporary artworks, its enigmatic visage continues to captivate and provoke thought, challenging societal norms.
Cultural References:
Baphomet has made appearances in films, literature, and television, often portrayed as a symbol of occult knowledge, rebellion, or an embodiment of esoteric secrets. Its presence in popular media adds layers of complexity to its cultural significance.
The Knights of the Templar
The Knights Templar, officially known as the Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, were a medieval Christian military order founded around 1119 CE. The order gained prominence during the Crusades, playing a significant role in the Holy Land and beyond.
Foundation and Purpose:
The Knights Templar were established by Hugues de Payens and Godfrey de Saint-Omer in Jerusalem. Their primary mission was to protect Christian pilgrims traveling to the Holy Land after its capture during the First Crusade. The order quickly expanded, acquiring considerable wealth and influence.
Military and Financial Power:
The Templars became renowned for their military prowess, disciplined structure, and distinctive white mantles adorned with a red cross. They developed a network of fortified castles across the Holy Land, effectively securing key routes for pilgrims.
In addition to their military role, the Templars became influential financiers. Pilgrims could deposit funds with the Templars in one location and receive a document that could be redeemed at another location, effectively creating a form of medieval banking.
Allegations and Dissolution:
The Templars’ rising wealth and influence attracted scrutiny. In the early 14th century, King Philip IV of France, facing financial difficulties, sought to eliminate his debts. In collaboration with Pope Clement V, he orchestrated a series of accusations against the Templars, including heresy, blasphemy, and idolatry.
Baphomet Allegations:
During the trials of the Templars, allegations emerged that the order worshipped a mysterious idol named Baphomet. The exact nature of Baphomet and whether it was a real idol or a fabrication by the Templars’ accusers remains a subject of historical debate.
Dissolution and Persecution:
In 1312, Pope Clement V disbanded the Knights Templar under pressure from King Philip IV. Many Templars were arrested, and trials were conducted to investigate the accusations. The order was officially dissolved, and numerous Templars faced persecution, including torture and execution.
Legacy
The legacy of the Knights Templar endures in popular culture, literature, and conspiracy theories. Their mysterious and abrupt dissolution, along with the allegations of secret rituals and hidden treasures, has fueled speculation and fascination throughout history.
Despite the controversial circumstances surrounding their demise, the Knights Templar left an indelible mark on medieval history and continue to captivate the imagination as legendary figures in the annals of chivalry and the Crusades.
Who is Baphomet?
Baphomet is an enigmatic and often misunderstood symbol in occultism, with historical connections to the Knights Templar and later adopted by various esoteric traditions.
What does Baphomet represent?
Baphomet represents an amalgamation of spiritual concepts, embodying elements of balance, duality, and esoteric wisdom. Its symbolism varies, with interpretations including alchemical unity and the reconciliation of opposites.
What is a Baphomet?
Baphomet is symbolically depicted as a humanoid figure with a goat's head, wings, and various occult symbols. It has been interpreted in different ways across occult traditions.
How to pronounce Baphomet?
It is pronounced as "BAH-foh-met" or "BAY-foh-may."
Who is Baphomet in Hindi?
The term "Baphomet" remains the same in Hindi.
What does Baphomet stand for?
Baphomet's symbolism stands for diverse esoteric principles, including spiritual balance, alchemical transformation, and hidden wisdom.
What does a Baphomet tattoo mean?
A Baphomet tattoo can convey individual beliefs, with meanings ranging from personal spiritual exploration to adherence to certain occult or esoteric ideologies.
Who is Baphomet Illuminati?
Baphomet is not a figure within the Illuminati, but conspiracy theories often incorrectly associate the symbol with secret societies.
How to summon Baphomet?
There is no credible or legitimate way to summon Baphomet. Such ideas are often rooted in fiction, occult fantasy, or conspiracy theories.
How to take the Baphomet oath?
There is no universally recognized Baphomet oath. Any claims related to such practices may be associated with specific esoteric groups, each with its unique rituals.
How to join Baphomet Illuminati?
Claims about joining the "Baphomet Illuminati" are typically part of online hoaxes or scams. The Illuminati, as commonly portrayed, does not involve Baphomet worship.
What are Baphomet rings?
Baphomet rings may feature the symbol as a design. Individuals wear them for personal reasons, often tied to their interpretation of Baphomet's symbolism.
What is Baphomet statue?
A Baphomet statue is a three-dimensional representation of the symbol, often used in esoteric or Satanic contexts.
What is the Baphomet Book Club?
There is no widely known "Baphomet Book Club." Specific groups or individuals may use the term for their private or esoteric reading circles.
What is Baphomet hand signs?
There is no established Baphomet hand sign. Claims about such signs are likely based on misinformation or conspiracy theories.
How to pray to Baphomet?
There is no standardized or recognized method for praying to Baphomet. Practices associated with Baphomet vary widely among different occult traditions.
What is a Baphomet costume?
A Baphomet costume typically involves dressing in attire inspired by the Baphomet symbol. It may be worn for personal expression or as part of occult-themed events.
What bible says about Baphomet?
The Bible does not mention Baphomet. The term "Baphomet" is not found in any biblical texts. The association of Baphomet with the Bible is a later development, particularly in the context of conspiracy theories, occultism, and various esoteric traditions. When examining biblical texts, there is no reference to the specific figure or symbolism associated with Baphomet as it is understood in modern occultism. The origins of the name and its connection to the Knights Templar trials in the 14th century are separate from biblical scripture.
Is Baphomet good or bad?
The interpretation of whether Baphomet is considered "good" or "bad" depends on the perspective and the cultural or religious context. Baphomet is a symbol that has been subject to various interpretations across different esoteric traditions, and opinions about its nature vary widely. It's important to note that Baphomet itself is a symbol, and its meaning can be influenced by individual beliefs, religious backgrounds, and cultural contexts.
In occult and mystical traditions:
Some see Baphomet as a symbol of balance, representing the reconciliation of opposites and the pursuit of spiritual enlightenment.
Others may view it as a representation of hidden wisdom and esoteric knowledge.
In popular culture and conspiracy theories:
Baphomet is sometimes portrayed as a demonic or Satanic figure, associated with dark or malevolent forces.
Certain conspiracy theories erroneously link Baphomet to secret societies, often perpetuating negative or sensationalized views.
Is Baphomet man or woman?
The traditional depiction of Baphomet often incorporates both masculine and feminine elements, presenting a figure that transcends gender distinctions. In the most famous illustration by the 19th-century occultist Eliphas Lévi, Baphomet is portrayed as a hermaphroditic being with both male and female characteristics. This symbolism aligns with the idea of reconciling opposites and achieving a harmonious balance.
The inclusion of both masculine and feminine features in Baphomet's representation emphasizes the concept of duality and unity, reflecting the alchemical principle of integrating opposing forces. As such, Baphomet is not exclusively identified as either a man or a woman but embodies a synthesis of both aspects to convey deeper spiritual and esoteric meanings.