Table of Contents
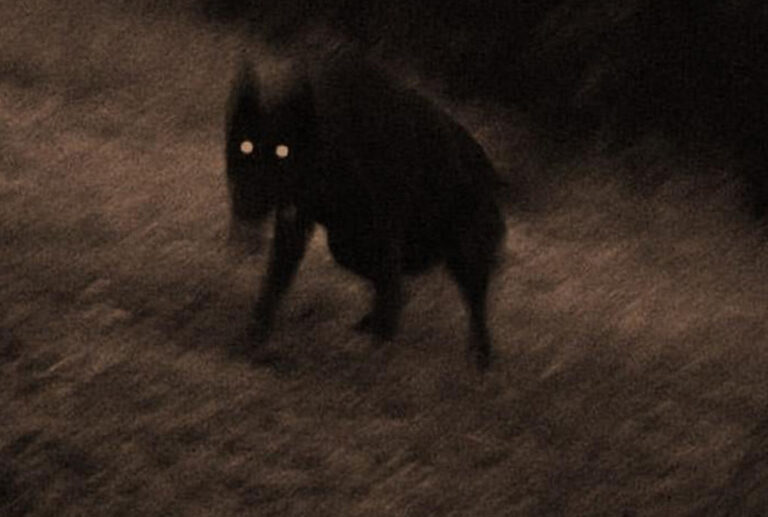
What is the Black Dog
The term “Black Dog” has various cultural and mythological associations across different societies. In mythology and folklore, the Black Dog is often depicted as a supernatural entity, typically with dark fur and glowing or fiery eyes. Different cultures have different interpretations and beliefs about the Black Dog, and its symbolism can vary widely.
British Folklore: In British folklore, the Black Dog is often considered a harbinger of death or a spectral omen. It is said to roam the countryside, especially at night, and encountering it is sometimes associated with impending misfortune or death.
Barghest: In northern English folklore, the Black Dog is sometimes referred to as the “Barghest.” The Barghest is a large, black, supernatural dog with huge teeth and claws. It is often associated with graveyards and is considered a guardian of the supernatural realm.
Celtic Mythology: In Celtic mythology, the Black Dog is sometimes seen as a spectral being or a shape-shifter. It may be associated with the Otherworld or the realm of the dead.
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s “The Hound of the Baskervilles”: While not strictly part of mythology, the famous Sherlock Holmes novel “The Hound of the Baskervilles” by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle features a large, supernatural black dog that haunts the Baskerville family.
Other Cultures: Similar black dog myths and legends can be found in other cultures, such as Scandinavian, Germanic, and American folklore, each with its own unique characteristics and interpretations.
Origin of Black Dog

The origin of the Black Dog legend is rooted in a combination of folklore, mythology, and cultural beliefs that have evolved over centuries. The specific origins can be challenging to pinpoint due to the widespread and diverse nature of these legends. Here are a few factors that may have contributed to the creation and spread of the Black Dog myth:
Cultural Beliefs:
Many cultures have historically associated black animals with superstitions and supernatural beliefs. Black is often seen as a color connected to mystery, the unknown, or the supernatural. This association may have contributed to the idea of a black dog being a harbinger of supernatural events.
Guardians of the Underworld:
In various mythologies, dogs are often associated with the afterlife or the underworld. The idea of a black dog as a guardian of the supernatural realm might have been influenced by these cultural and religious beliefs.
Nightmares and Nightly Apparitions:
Black Dogs are often said to be seen at night, which could be linked to the fear and mystery associated with darkness. Nighttime experiences and the tendency of the human mind to interpret shadows and sounds might have contributed to the creation of stories involving spectral black dogs.
Literary Influences:
Literary works, including folklore, myths, and later fiction, have played a significant role in shaping and popularizing the Black Dog legend. Stories such as the Barghest in northern English folklore and Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s “The Hound of the Baskervilles” have contributed to the enduring image of the Black Dog.
Historical Events and Tragedies:
Some local legends of Black Dogs are said to be associated with historical events or tragedies. The appearance of a black dog might be linked to misfortunes or disasters, leading to the incorporation of the legend into local folklore.
Psychological and Sociological Factors:
The human mind’s tendency to seek patterns and make connections, as well as societal fears and anxieties, can contribute to the creation and perpetuation of supernatural legends. These factors may have played a role in the development of the Black Dog myth.
The Black Dog legend, in its various forms across different cultures, continues to capture the imagination and persists as a part of cultural heritage and storytelling traditions. The specific details of the legend may vary, but the common theme of a mysterious and often supernatural black dog endures in folklore worldwide.
History

The history of the Black Dog legend is deeply rooted in folklore, mythology, and cultural traditions. While it’s challenging to pinpoint a specific origin, as the legend has evolved over centuries and across different cultures, we can explore some historical aspects and notable mentions of Black Dogs in various contexts:
Ancient Cultures:
The association of dogs with the supernatural or divine can be traced back to ancient cultures. In Greek and Roman mythology, for example, dogs were often linked to the underworld and were believed to guide souls to the afterlife. This association could have influenced later beliefs in different cultures.
Celtic and Norse Influences:
In Celtic and Norse mythology, dogs were often seen as creatures with mystical qualities. These cultures had beliefs in shape-shifting entities, and dogs were sometimes considered guardians or companions of the Otherworld. This could have contributed to the development of Black Dog legends.
Medieval Europe:
During medieval times in Europe, Black Dogs became prominent figures in folklore. They were often associated with the Devil or other supernatural forces. The belief that encountering a Black Dog was an omen of death or misfortune gained traction during this period.
Church and Folklore:
The influence of Christian beliefs also played a role in shaping the perception of Black Dogs. In some cases, these dogs were thought to be demonic or hellhounds. The appearance of Black Dogs near churches or graveyards became a common theme in folklore.
Literary Contributions:
The Black Dog legend found its way into literature, further solidifying its place in cultural storytelling. Notable examples include the Barghest in northern English folklore and Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s “The Hound of the Baskervilles,” a Sherlock Holmes novel that features a spectral black dog.
Regional Variations:
The Black Dog legend has regional variations with unique characteristics and interpretations. Different areas developed their own stories and beliefs surrounding these mysterious creatures, often influenced by local history, geography, and cultural practices.
Symbolism in Art and Culture:
The Black Dog has been depicted in various forms of art, including paintings, sculptures, and literature. Its symbolism often reflects cultural attitudes towards death, the supernatural, and the unknown.
Black dog in popular culture

The black dog has made its mark in popular culture, appearing in various forms across literature, music, film, and other media. Here are some notable examples:
Literature:
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s “The Hound of the Baskervilles” (1902): One of the most famous instances of a black dog in literature, this Sherlock Holmes novel features a phantom black hound that haunts the Baskerville family.
Harry Potter Series by J.K. Rowling: The Grim is a spectral dog that is an omen of death. While it can take various forms, it is often described as a large black dog.
Neil Gaiman’s “American Gods” (2001): Black dogs appear in Gaiman’s novel as supernatural entities, serving various mythological roles.
Music:
Led Zeppelin’s “Black Dog” (1971): The iconic rock band Led Zeppelin released a song titled “Black Dog.” While the lyrics don’t specifically refer to a literal black dog, the term is used metaphorically to describe a problematic relationship.
Nick Drake’s “Black Eyed Dog” (recorded in 1974, released posthumously): This haunting song by Nick Drake uses the image of a black-eyed dog as a metaphor for depression.
Film and Television:
“The Omen” (1976): In this horror film, a large black dog appears as a demonic entity associated with the Antichrist.
“Supernatural” (TV series, 2005-2020): The show features a recurring character called the Hellhound, a black dog sent by demons to collect souls.
Mental Health Metaphor:
The term “black dog” has been popularized as a metaphor for depression, particularly after it was associated with Sir Winston Churchill. This metaphor has been used in various campaigns to raise awareness about mental health.
Folklore and Urban Legends:
The black dog continues to be part of local folklore and urban legends in various regions, with stories passed down through generations.
Video Games:
“Fable II” (2008): This action role-playing game features a character known as the “Black Dog,” representing a manifestation of the protagonist’s guilt and moral choices.
The black dog’s presence in popular culture is diverse, ranging from traditional folklore to modern metaphors for mental health. Its symbolism often carries a sense of mystery, foreboding, or supernatural significance, making it a versatile element in storytelling across different mediums.
What does a black dog mean in folklore?
In folklore, a black dog is a common motif that varies in symbolism across different cultures. Generally, black dogs are associated with the supernatural and are often considered omens. They can be seen as both benevolent and malevolent, representing either protection and guidance or as harbingers of death and misfortune.
What do black dogs symbolize?
The symbolism of black dogs varies but often includes elements of mystery, protection, and the supernatural. In some cases, they symbolize death or the afterlife, while in others, they represent guardianship or loyalty. The interpretation depends on cultural context and specific folklore or mythology.
What is the black dog theory?
The "black dog theory" is not a widely recognized concept. However, if you're referring to the metaphorical use of the term "black dog" as a symbol for depression, it gained prominence in discussions about mental health. The idea is often attributed to Sir Winston Churchill, who used the term to describe his struggles with depression.
What is the story of the black dogs?
The stories of black dogs vary widely across different cultures and regions. They are often featured in folklore as supernatural entities, appearing as both protectors and omens of doom. Specific stories may include encounters with black dogs in certain locations, with the outcome reflecting the dog's benevolent or malevolent nature.
What do black dogs symbolize in literature?
In literature, black dogs can symbolize a range of themes, including mystery, the supernatural, and symbolism related to death or forewarning. The interpretation often depends on the context of the story and the cultural or mythological influences shaping the narrative.
What is the black dog in Chinese mythology?
In Chinese mythology, black dogs are not as prevalent as in Western folklore. However, there are stories and beliefs related to black dogs in various cultural contexts within China. The interpretation can vary, but they may be associated with protection or mythical elements.
Is a black dog good luck?
The perception of black dogs as good luck or bad luck depends on cultural beliefs. In some cultures, black dogs are considered protectors and bringers of good fortune, while in others, they may be seen as omens of misfortune or death.
What gods are associated with black dogs?
Specific gods associated with black dogs vary across cultures. In some mythologies, gods may have animal companions, including black dogs, that symbolize various qualities such as protection, guidance, or other supernatural attributes.
Why is it called the black dog?
The term "black dog" likely originated from the physical appearance of dark-furred dogs. The use of this term in folklore and literature may have been influenced by the association of the color black with mystery and the unknown.
What do dogs represent in folklore?
Dogs in folklore often represent loyalty, companionship, and protection. They can also be seen as guides to the afterlife or as supernatural entities. The cultural significance of dogs in folklore varies, with stories reflecting the roles and characteristics attributed to them in different societies.